Dementia is a mental cognitive disease in which a person lost his memory and finds difficulty in thinking interpreting analysing and reasoning.
This malfunctioning of the brain affects the day-to-day life of an individual to such an extent that they are unable to control their emotions, hesitate in speaking and many more which leads to changes in their personality.
In general, dementia is a broad term that includes most brain-related disorders. As we know the brain is the main functioning unit in our body, hence if a person suffers from any brain-related problem, then it is obvious that he seems to be enabled in solving problems, taking decisions and handling feelings. Due to this factor, many times dementia arises with the question that it is a disease, inability or anything else?
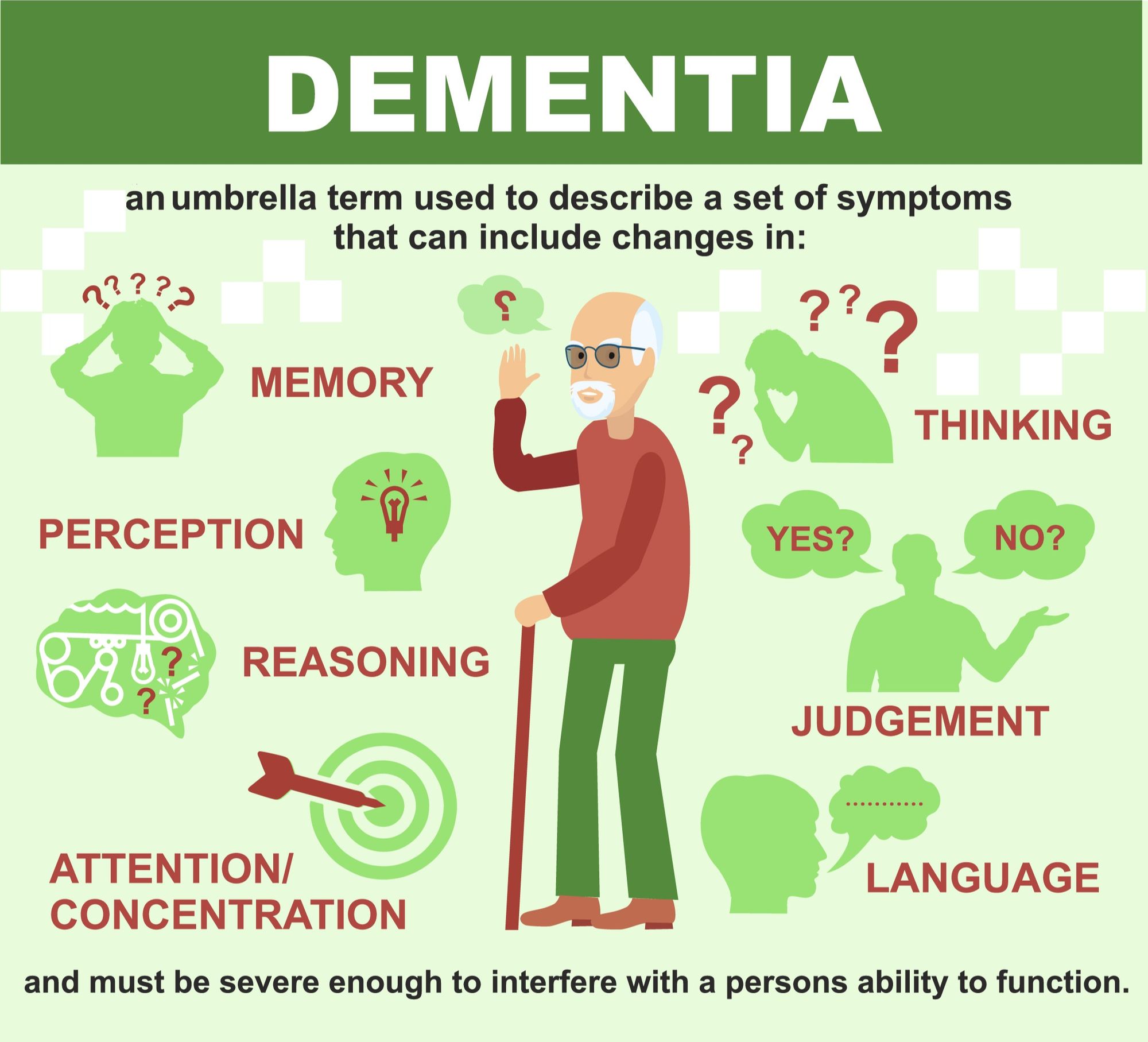
No dementia is not categorised as a specific disease or inability. It is an umbrella term used to define or express the impaired ability of a person to remember, think, analyse and interpret.
Types of dementia

Alzheimer’s disease:
(This is the most common cause of dementia.
Although not all causes of Alzheimer’s disease are known, experts do know that a small percentage are related to mutations of three genes, which can be passed down from parent to child. While several genes are probably involved in Alzheimer’s disease, one important gene that increases risk is apolipoprotein E4.
Alzheimer’s disease patients have plaques and tangles in their brains. Plaques are clumps of a protein called beta-amyloid, and tangles are fibrous tangles made up of tau protein. It’s thought that these clumps damage healthy neurons and the fibers connecting them.) Https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions
Vascular dementia:
In vascular dementia whether death transfer blood to the brain gets damaged and this damage harm the brain fibre present in the white matter of the brain.
The most common signs of vascular dementia include difficulties with problem-solving, slowed thinking, and loss of focus and organization. These tend to be more noticeable than memory loss.
(Lewy bodies are abnormal balloon-like clumps of protein that have been found in the brains of people with Lewy body dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. This is one of the more common types of progressive dementia.
Lewy body dementia:
Common signs and symptoms include acting out one’s dreams in sleep, seeing things that aren’t there (visual hallucinations), and problems with focus and attention. Other signs include uncoordinated or slow movement, tremors, and rigidity (parkinsonism).
Frontotemporal dementia:
This is a group of diseases characterized by the breakdown of nerve cells and their connections in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These are the areas generally associated with personality, behaviour and language. Common symptoms affect behaviour, personality, thinking, judgment, language and movement.
Mixed dementia:
Autopsy studies of the brains of people 80 and older who had dementia indicate that many had a combination of several causes, such as Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia and Lewy body dementia. Studies are ongoing to determine how having mixed dementia affects symptoms and treatments. (Mayo Clinic)
All these diseases of dementia are irreversible but by treatment, one can limit the damage.
Stages of dementia

Also Read : The Big Bull: Rakesh Jhunjhunwala
No impairment
In this one may not find that anything is happening wrong with him. One feels that he is absolutely fine but the report shows that person is suffering from dementia.
Very mild decline
In this, a person finds a little bit of problem in his thinking and reasoning but for other people, he seems to be normal.
Mild decline
In this, a person notices problems and troubles in making plans, in taking decisions, in thinking and reasoning. The difference in the scenario before and after dementia can be easily noticed by an individual
Modern decline
One can have serious problems in organising recent events. This also involves a little bit of loss of memory and one may have a hard time with travelling and handling. Many times, this stage involved a change in personality and behaviour due to which it can be noticed by others easily also.
Moderately severe decline
In Moderate severe decline, people may not remember their phone number or their grandchildren’s names. They may be confused about the time of day or day of the week. At this point, they’ll need assistance with some basic day-to-day functions, such as picking out clothes to wear.
Severe decline
In severe decline person lost his memory entirely. He is unable to recognise their loved ones and require assistance in walking and eating.
Very severe decline
In very severe decline person is unable to express his thoughts, brain nullified by itself which stop communication and person wants to spend most of his time on the bed.
Causes of dementia
Dementia is caused by damage to Nerve cells of the brain. Since, a different part of the brain is responsible for different functioning like making decisions, memory and making plan etc. Damage to a particular part affects the specific traits of an individual. This damage can be caused due to the following reasons
- Brain injury
- Depression
- Excess use of alcohol.
- Thyroid problems.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Infections and immune disorders
- Metabolic problems and endocrine abnormalities
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Medication side effects
- Subdural hematomas
- Brain tumours
- Normal-pressure hydrocephalus
Symptoms of dementia

All symptoms and signs of dementia are connected to a person’s cognition and psychology. These symptoms may vary with stage and type of dementia.
Here are some common symptoms:
- Memory loss, which is usually noticed by someone else
- Difficulty communicating or finding words
- Difficulty with visual and spatial abilities, such as getting lost while driving
- Difficulty reasoning or problem-solving
- Difficulty handling complex tasks
- Difficulty with planning and organizing
- Difficulty with coordination and motor functions
- Confusion and disorientation
- Personality changes
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Inappropriate behaviour
- Paranoia
- Agitation
- Hallucinations
Treatment
Since most dementia cases are irreversible, no medication can cure them but with a ray of hope there are some treatments and therapies which can reduce the symptoms and limit the damages and here they are:
Reminiscence therapy
In this, the concerned person is asked to spend some time with his past colleagues who are very near and dear to him and try to recognise him /her about past days like school life, common friends, fun and fall of that time. This involves going to their hometown and making him recognise others with past photos and incidents. Some of their favourite tasks of their past life remind any anecdotes. This will help an individual to recognise all the things that he had forgotten due to dementia.
Cognitive stimulation therapy
Cognitive stimulation therapy is a structured program for a group of people who belong to the stage of mild and moderate dementia.
In cognitive stimulation therapy, we make a person involved in mental and communicative activities like talking about current events, singing, playing word games, or cooking from a recipe.
Reality orientation training
Reality orientation is a technique used with disabled veterans to help them engage in and connect with, their surroundings. It’s an approach where the environment, including dates, locations, and current surroundings, is frequently pointed out and woven into the conversations with the person. Reality orientation, when used appropriately and with compassion, can also benefit those living with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
Lifestyle
Dementia sufferers should be well cared for with their lifestyle. They should take proper diet, prioritise good sleep, maintain good eating habits, do regular exercises, stay actively involved in gathering, go for timely counselling or check-up, playing brain cell in these games.
Prevention
Since we all know that “Prevention is better than cure”. So, we come up with preventions to avoid such chronic disorders or diseases:
- Keep your mind active
- Be physically and socially active
- Quit smoking
- Get enough vitamins
- Manage cardiovascular risk factors
- Treat health conditions
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Get good-quality sleep
Further Reading :