In the digital era, privacy must be the topmost priority. Whether you have high knowledge in technology or just cautious, you might be thinking of yourself as having cyber acumen.
But most of us have unknowingly had our cyber safety menace.
Your personal information isn’t secure. It can be destroyed anytime, or you can lose your identity, savings, livelihood, or worse.
But, with some security threats and cautions, we can protect our information, and can easily bear the scammers at their game! Here are nine quick, easy steps to protect yourself from cybercrime.
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is any criminal activity that either uses or targets a computer, a networked device, or a computer network.
It is carried out by individuals or organizations. Cybercriminals commit cyber crimes to make money through scams.
Some cybercriminals possess high expertise, while some are novice hackers.
Cybercriminals with high expertise have advanced strategies to implement and are technically skilled.
Hardly, apart from profit, cybercrimes aim to damage computers for reasons, could be personal or political.
Types of Cybercrime

Cybercrime is not a single way to get users into a trap or to hack their computers. Here are some different types of cybercrimes:
- Identity information (risk of stolen or use of personal information)
- Internet and Email fraud
- Theft of financial or card payment data.
- Sale and theft of corporate data.
- Cyber Exaction (demanding money to prevent a threatened attack).
- Ransomware attacks (similar to cyber exaction)
- Cryptojacking (Hackers mine cryptocurrency using resources they don’t possess)
- Cyber Espionage (Hackers access company or government data)
Most, but not all, cybercrime falls under these two categories:
- Criminal activity that targets, and
- Criminal activity requires a computer to commit crimes.
The Criminal activity that targets computers often includes viruses and various types of malware.
Cybercriminal may infect computers with malware and viruses to damage devices or to stop them from damaging them. Malware can be used to steal or delete data.
Cybercrimes that stops devices from working, stops users using a network or machine, or prevents software services provided by a company to its customers, is also known as a Denial-of-service (DoS) attack.
Criminal activity that requires a computer to commit crimes may include using computers spreading malware, illegal images, or information.
the Cybercriminals sometimes conduct both types of cybercrime at a time.
They use computers with viruses first and then use them to spread malware throughout a network.
Cybercriminals also carry out the Distributed-Denial-of-service (DDoS) attack. It is similar to a DoS attack, but DDoS requires numerous compromised computers to carry out.
Examples of Cybercrime
Here are some famous examples of cybercrime attacks used by cybercriminals.
- Malware Attacks
- Phishing
- Distributed DoS attacks
Malware Attacks
Malware attacks are where a computer network or system with a type of malware or with a computer virus.
Cybercriminals use a computer with malware for various purposes. It includes using the computer to carry out criminal acts, stealing confidential data, or causing damage to data.
An example of a malware attack is the global cybercrime conducted in May 2017, named the WannaCry ransomware attack.

They used the ransomware attack to extract money by possessing the victim’s device or data to ransom.
WannaCry is a type of ransomware attack that targeted a computer’s vulnerability running MS Windows.
This attack affected 230,000 computers in around 150 countries. It locked the users out from their files and delivered a message to pay a Bitcoin ransom to regain access to their data or files.
This attack caused a financial loss of around $4 billion worldwide.
Phishing
Phishing is when spam emails, or other forms of communication, were sent to trick the recipient into doing something that erodes the individual’s security or organization’s security they work in.
An example of Phishing is in 2018, which took place over the World Cup. As per report, this Phishing scam included emails sent to football fans.
Through these spam emails, they tempt the fans to make fake trips to Moscow, where the World Cup was going to host. Those who clicked on the link included in the emails had stolen their data.
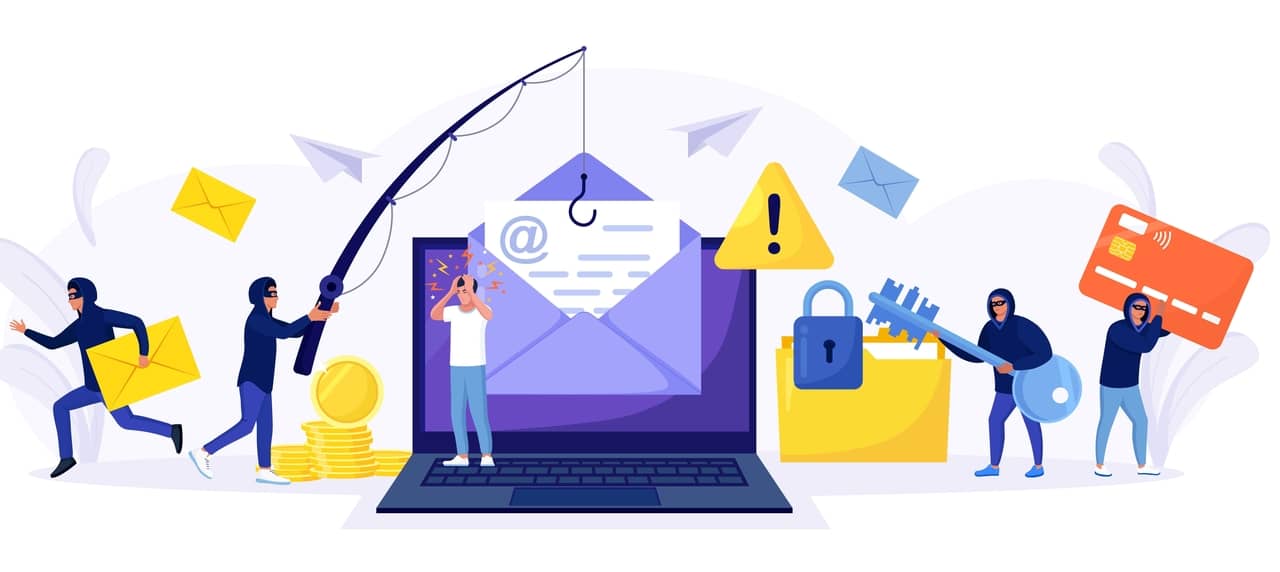

Another phishing campaign, known as spear-phishing campaign. These campaigns were to trick specific individuals into imperilling the organization’s security they work in.
Quite different from mass phishing campaigns, they craft spear-phishing messages to look like messages received from a trusted source; they didn’t contain any visual clues that they were spamming.
Also Read: Cybersecurity: How Ransomware Sneaks In?
Distributed DoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are a type of cybercrime attack that hackers use to bring down a network or system. They use IoT (Internet of Things) devices for launching DDoS attacks.
A DDoS attack submerges a system by using one of the standard communication protocols to spam the system having connection requests.
Cybercriminals who carry out the cyber exaction use a threat of DDoS attack to demand money.
Instead, they used a DDoS attack as a distraction tactic when other cybercrimes took place.
An example of a DDoS attack has occurred in the UK, The National Lottery websites and Apps, we’re prevented from UK citizens to play.
9 Tips to Keep Yourself Safe From Cybercrime
Cybercrime is the biggest threat. Anyone using the internet should exercise some precautions to protect themselves from cybercrime.
Here are 9 tips to follow against the range of cybercrimes out there.
1. Use Full-Service Internet Security Suite
Use real-time protection against emerging and existing malware including viruses and ransomware, and protect your financial or personal information when you go online either on social media or any other site.

2. Always Use Strong Passwords
Remember not to repeat the same passwords on different sites. Update them regularly and make them complex, i.e., using a password containing symbols, 10 letters, and numbers.

An application for password management also helps to keep strong passwords locked down.
3. Update Software
Keep your system software updated, especially for software of internet security and operating systems.

Hackers use known flaws, exploits, in your system software to hack your system. Mending those flaws and exploits can help you protect yourself from cybercrime.
4. Manage Social Media Settings
While updating profiles, keep your personal and financial information locked down.

Social engineering cybercriminals can get your whole data with just a few data points. The less you share publicly, the more your information is secure.
5. Strength Home Network
Start with a strong virtual private network (VPN) and encryption password. A VPN will encrypt all traffic that leaves your devices until it reaches its final destination.

If a hacker somehow hacked your communication line, they will intercept encrypted data. So, while using a public Wi-Fi network, either in a library, café, airport, or hotel, use a strong VPN.
6. Major Security Breaches
It’s good to stay up to date on major security breaches.

If you have an account on a website, or you do business with a merchant that’s been influenced by a security breach, know all the information that hackers access, update it and change the site’s password immediately.
7. Protection From Identity Theft
Take certain measures to protect yourself from identity theft. It occurs when cybercriminals try to obtain your private data in a fraud or deception way, to have some financial gain.

You might get tricked or a hacker might steal your mail to grant access to your account information.
8. Keep an Eye on Kids
Identity thieves mostly target children, as their credit histories and social security number easily represent a clean slate.

Teach them about how they can be tricked. You can prevent identity theft by being cautious while sharing a child’s personal information.
9. Know How to React if you become a victim
If you believe that you have become a victim, you have to alert the local police as soon as possible, or the FBI and Federal Trade Commission.

It is a must, even if you find it a minor crime. Your report will help to thwart criminals from not taking advantage of any other people in the future.
Consider these steps if you find your identity stolen.
- Contact the banks and companies where you find the fraud occurred.
- Get your credit reports and place the fraud alerts.
Conclusion
No doubt, there’s much more an organization or an individual can do to protect their data. After all, at the end of the day, our primary goals are simple: security and safety.
To protect yourself from data breaches at places where you store your information, you should freeze your credit, which will black anyone from applying for a transaction in your name without your permission.
If you already received the notification that your data gets stolen, put a free “fraud alert” on your credit reports.
No organization, computer, or individual can ever be fully secure. Even a person with good technical skills, and money can get into the trap of cybercrime.
By following the above-mentioned steps, you can protect yourself from being a victim, in both terms online and offline.
Further Reading:




